Each person in a workplace has a specific job to do, and each person holds a specific role in the hierarchy of authority and decision-making for that particular workplace. Workers are expected to know how to address a supervisor, what tone of voice and body language to use when responding to customer requests, what kinds of conversations are appropriate in the work environment and the break room, and a host of other unwritten social “rules.” A worker who doesn’t understand and follow those rules may be at risk for losing his job. For some students, it is helpful to translate these unwritten rules into explicit rules, with clear examples for the kind of behavior that is expected in each social encounter. A student can then practice responding to a customer’s question or a supervisor’s comments with concrete responses that will help minimize conflict and maintain the student’s good standing in the workplace.
Labeling Roles & Expectations
 Guiding Questions
Guiding Questions
- Does the student demonstrate understanding of authority through his actions and words?
- Where does the student act respectfully? What are the settings and the people with whom the student behaves with (relative) courtesy?
- How well does the student differentiate peer interactions and teacher interactions?
- Are there differences in the student’s interaction pattern with his parents?
Visual Supports

Communication systems and scripts provide the student with a means to initiate communication. Use these cards to practice different scenarios with your students.
|
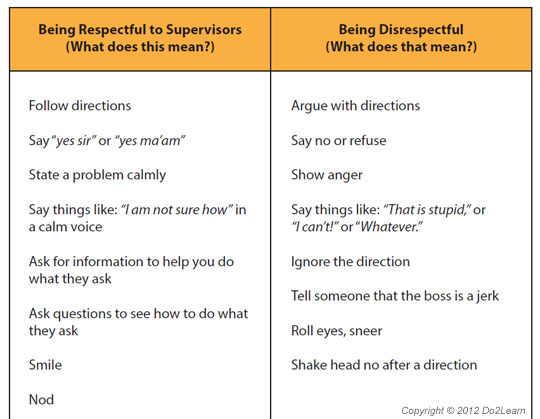
Graphic organizers can provide a student with a way to represent and organize concepts, thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and potential outcomes.
|
|
Social narratives are a set of tools that visually represent social situations and appropriate social behaviors. The social narrative connects the important details of a setting or social situation to support the student in understanding the social context and in developing a new social skill.
|

Visual Cues are learning materials that students can keep with them to help guide them through real life situations.
|

Video modeling involves the use of video recording as a teaching tool. It involves a student watching a video of the appropriate performance of a task (expected behavior) prior to practicing or potentially using the skill in natural settings.
|









