Everyone makes mistakes. It is a crucial skill for an employee to know how to deal with and move on from their mistakes in a positive way. The employee must listen to the negative feedback, process any suggestions for how to avoid another mistake, make any necessary apologies, and commit to rectifying the mistake. They must do all of this while remaining calm, polite, and keeping things in perspective. This is a hard task for anyone! Instructors should work with students to help them understand the need for occasional negative feedback, the perspective of the critic, and how best to handle criticism. Practicing these skills will help the student weather their mistakes in a productive way.
Accepting Negative Feedback & Handling Mistakes
 Guiding Questions
Guiding Questions
- Can the student self-calm?
- Can the student attend to the feedback and understand the comment?
- Can the student read the non-verbal cues correctly?
- Can the student determine the role of the speaker or critic?
- Can the student label the criticism and apologize for the mistake?
- Can the student engage in a negotiated plan that helps prevent future errors?
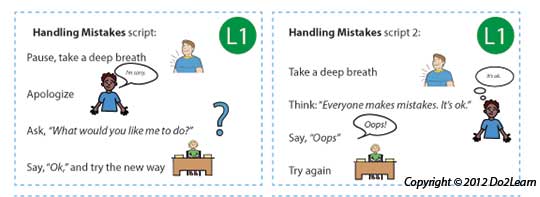
Communication systems and scripts provide the student with a means to initiate communication. Use these cards to practice different scenarios with your students.
|
|
Schedules are visual supports that organize the school or work day and tell the student where he will go that day. Schedules help focus attention on the sequence of places and events.
|
|
The to-do list (also referred to as a "work system"or "activity system") visually clarifies a series of activities that a student is to do.
|
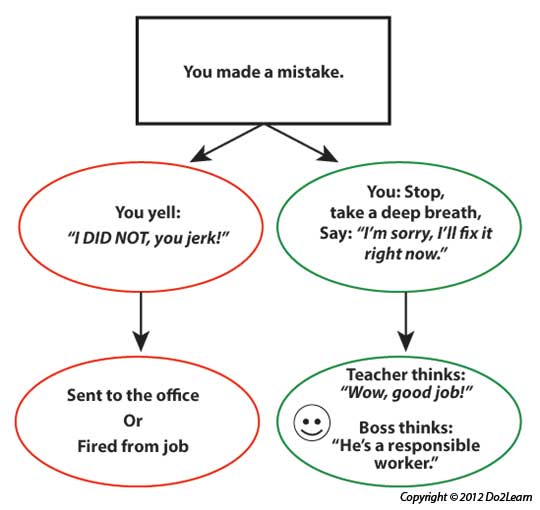
Graphic organizers can provide a student with a way to represent and organize concepts, thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and potential outcomes.
|

Social narratives are a set of tools that visually represent social situations and appropriate social behaviors. The social narrative connects the important details of a setting or social situation to support the student in understanding the social context and in developing a new social skill.
|

Visual Cues are learning materials that students can keep with them to help guide them through real life situations.
|
Video modeling involves the use of video recording as a teaching tool. It involves a student watching a video of the appropriate performance of a task (expected behavior) prior to practicing or potentially using the skill in natural settings.
|
 Does the design of space and furniture help the student focus on the tasks and behaviors expected in the setting? Does the environmental design address student issues with proximity to others or even distractibility that may reduce performance (working close to others may set up too much interaction)? The student may have a more difficult time accepting negative feedback or handling mistakes in a large class or work environment with multiple co-workers in close proximity. Consider whether the student’s desk should be moved to the back of the room so he has an easier time reacting to this feedback with less distractions or a “smaller audience”. Maybe the student needs to be assigned tasks or areas on the job site that have limited customer interaction to reduce the possibility of needing to deal with customer complaints. It may help to have his assigned area close to an experienced co-worker or supervisor that he could easily refer customers to for assistance. Are there clear separate spaces for different contexts or sets of activities (i.e., place to take a break vs. work spaces vs. place for belongings, etc.)? In most cases, negative feedback should be delivered in private, particularly as the student is learning to appropriately respond. Wouldn’t we all prefer to receive negative feedback away from our peers and others? |











