Change is a fact of life. Even in jobs with fairly predictable schedules, work times, co-workers, supervisors, and responsibilities may change. Some students may be very upset about these changes, and becoming a good employee means developing strategies to deal with change as it arises. Having a “cool-down plan” can help a student maintain composure when faced with an unexpected change. Students should also be encouraged to think about why changes happen, and that they are a normal and important part of everyday life. Although some students may need significant support and reassurance during a major change in the workplace, many students can develop the coping skills necessary to take changes in stride.
Tolerating Changes
 Guiding Questions
Guiding Questions
- Can the student identify or label ‘change’ when it occurs?
- How does the student respond to changes in their schedule?
- How does the student respond if you change the sequence of events on their schedule or to-do list?
- How does the student respond to new people (new co-workers/supervisors or new students/teachers) or new locations?
- How does the student handle added tasks or responsibilities?
- Does the student seem to benefit from advanced warning of changes or does this make them more anxious?
Visual Supports
|
Schedules are visual supports that organize the school or work day and tell the student where he will go that day. Schedules help focus attention on the sequence of places and events.
|
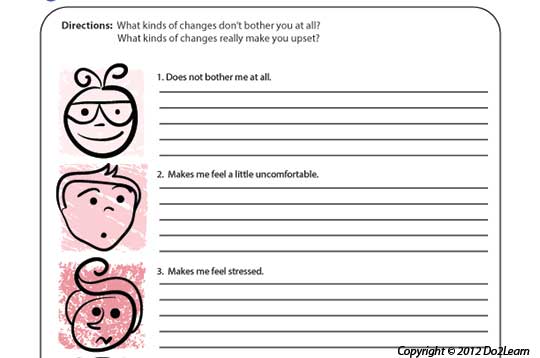
Graphic organizers can provide a student with a way to represent and organize concepts, thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and potential outcomes.
|

Social narratives are a set of tools that visually represent social situations and appropriate social behaviors. The social narrative connects the important details of a setting or social situation to support the student in understanding the social context and in developing a new social skill.
|
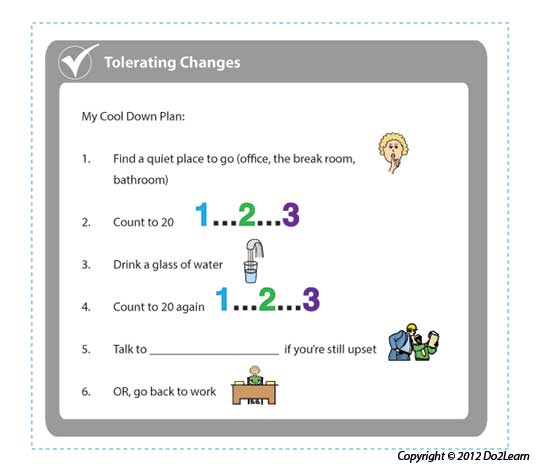
Visual Cues are learning materials that students can keep with them to help guide them through real life situations.
|
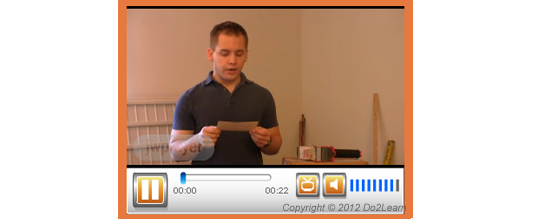
Video modeling involves the use of video recording as a teaching tool. It involves a student watching a video of the appropriate performance of a task (expected behavior) prior to practicing or potentially using the skill in natural settings.
|









